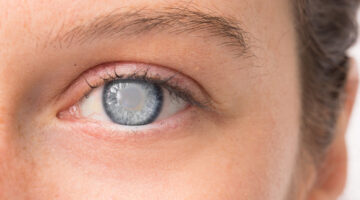
Cataracts are a prevalent eye condition that can impact anyone, especially as they age. While cataracts all involve clouding of the eye’s natural lens, there are different types, each with distinct characteristics and causes. In this blog post, we’ll explore the three most common types of cataracts, shedding light on their unique features and how they affect your vision.
Nuclear Cataracts
Nuclear cataracts are the most common type and typically associated with aging. They develop deep within the central or “nuclear” part of the eye’s lens. Over time, the lens becomes denser and yellower, causing the following changes in vision:
- Near Vision Improvement: In the early stages, nuclear cataracts can actually enhance your near vision temporarily, known as “second sight.” This can make reading without glasses easier for a brief period.
- Blurry Vision: As the cataract progresses, your vision becomes increasingly blurry, making it challenging to see distant objects clearly.
- Yellowing of Vision: Colors may appear more faded or yellowed due to the discoloration of the lens.
Cortical Cataracts
Cortical cataracts form as wedge-shaped opacities on the outer edges of the lens, starting at its periphery and gradually extending towards the center. This type of cataract often looks like spokes of a wheel. The symptoms associated with cortical cataracts include:
- Glare and Halos: When light enters the eye, it scatters around the edges of the cataract, causing glare and halos around lights, particularly at night.
- Blurred Vision: The spoke-like opacities can cause blurred or distorted vision, making it difficult to read or see clearly.
Posterior Subcapsular Cataracts
Posterior subcapsular cataracts occur at the back of the lens, just beneath the lens capsule. Unlike the other types, these cataracts tend to progress rapidly and affect vision in unique ways:
- Glare and Halos: Similar to cortical cataracts, this type can cause glare, halos, and difficulty seeing at night.
- Difficulty with Reading and Close Work: Posterior subcapsular cataracts often impact the ability to focus on near objects, such as reading or using electronic devices.
- Vision Changes in Bright Light: Bright light sources, such as sunlight or headlights, can exacerbate vision problems and discomfort.
While these are the most common types of cataracts, it’s essential to remember that cataracts can vary in severity and presentation. If you notice changes in your vision, such as blurriness, glare, or difficulty with color perception, it’s crucial to consult with an eye care specialist. Early detection and treatment are key to effectively managing cataracts and preserving your visual clarity. Fortunately, cataract surgery is a highly successful procedure, and with the right guidance, you can regain clear and vibrant vision. Don’t hesitate to reach out to an eye care professional to discuss your concerns and explore your treatment options.